Advanced Process Modeling and Simulation for Bioprocessing Training Course
Advanced Process Modeling and Simulation for Bioprocessing Training Course offers a deep dive into the mathematical, data-driven, and computational techniques required to build, calibrate, and validate high-fidelity models for both upstream and downstream unit operations.
Skills Covered
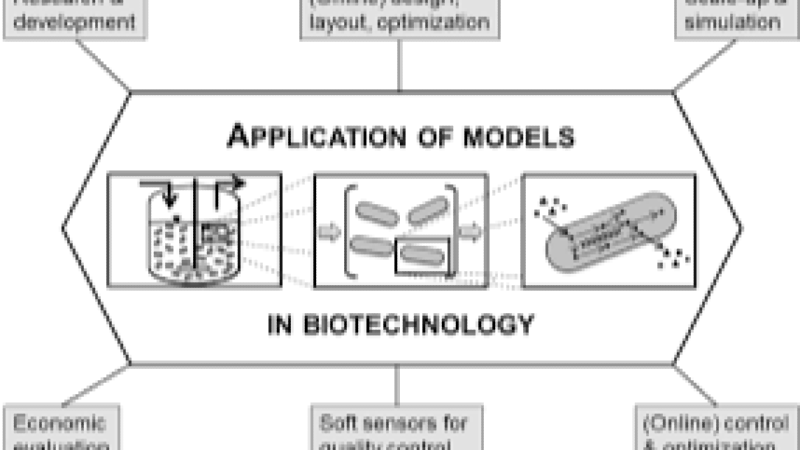
Course Overview
Advanced Process Modeling and Simulation for Bioprocessing Training Course
Introduction
The biopharmaceutical industry is in the midst of a rapid Digital Transformation, moving beyond traditional empirical methods to embrace Biomanufacturing 4.0 principles. Advanced Process Modeling (APM) and Simulation are now indispensable tools for modern bioprocess development, enabling scientists and engineers to virtually represent, predict, and optimize complex biological and physicochemical phenomena. This shift from costly, time-consuming lab experiments to an efficient Virtual Process Environment is critical for establishing robust Quality by Design (QbD) frameworks, accelerating drug development timelines, and ensuring continuous process verification in high-stakes environments like Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT) manufacturing. Mastery of these computational tools including Mechanistic Modeling, Hybrid Models, and the deployment of Digital Twins is no longer a niche skill but a core competency for driving Process Intensification and achieving cost-effective, sustainable bioproduction.
Advanced Process Modeling and Simulation for Bioprocessing Training Course offers a deep dive into the mathematical, data-driven, and computational techniques required to build, calibrate, and validate high-fidelity models for both upstream and downstream unit operations. Participants will gain hands-on expertise with industry-leading simulation platforms, learning to integrate Machine Learning (ML) and first-principles knowledge to enhance predictive accuracy. By focusing on model-based strategies for Scale-Up, Techno-Economic Analysis (TEA), and Advanced Process Control (APC), this training directly equips professionals to slash R&D time, minimize batch-to-batch variability, and identify process bottlenecks early, ultimately leading to faster delivery of life-saving therapeutics.
Course Duration
10 days
Course Objectives
Upon completion, participants will be able to:
- Develop and calibrate high-fidelity Mechanistic Models for complex bioreactor kinetics and mass transfer.
- Implement Digital Twin frameworks for real-time monitoring and predictive process control.
- Design and validate Hybrid Modeling approaches that combine First-Principles with Machine Learning (ML) for enhanced prediction accuracy.
- Apply Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) principles to optimize mixing and shear stress in large-scale vessels.
- Formulate and deploy Soft Sensors for real-time estimation of Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs).
- Drive Quality by Design (QbD) initiatives by using models to define the Design Space and robust control strategies.
- Perform comprehensive Techno-Economic Analysis (TEA) and Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) modeling using simulation tools.
- Master model-based Scale-Up and Scale-Down methodologies to ensure successful Technology Transfer.
- Configure and leverage commercial simulation platforms for entire Flowsheet Modeling.
- Design and optimize Continuous Bioprocessing systems, including perfusion and multi-column chromatography, via simulation.
- Apply Advanced Process Control (APC) strategies, specifically Model Predictive Control (MPC), for dynamic process optimization.
- Conduct rigorous Parameter Estimation and Model Validation against experimental and manufacturing data.
- Evaluate the unique modeling requirements and complexities for Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT) manufacturing processes.
Target Audience
- Bioprocess Engineers (R&D, Process Development, Manufacturing Support)
- Data Scientists/Engineers focused on biomanufacturing Digitalization initiatives
- Automation & Control Engineers implementing APC in biopharma facilities
- Research Scientists and Principal Investigators in biopharma and academia
- Process Development Scientists focusing on QbD and process characterization
- Technology Transfer Specialists
- Managers/Supervisors
- Chemical/Biochemical Engineers
Course Modules
1. Fundamentals of Bioprocess Modeling & Quality by Design (QbD)
- Biomanufacturing 4.0 and the role of in-silico tools.
- Classification of models.
- Review of mass, energy, and momentum balances.
- Defining CQAs and CPPs in a model-centric QbD framework.
- Case Study: Developing a simple Monod kinetics model for a batch fed-batch bioreactor to predict glucose and biomass profiles.
2. Advanced Mechanistic Modeling of Upstream Processes (USP)
- Formulation of structured and unstructured bioreactor kinetics models.
- Modeling multi-substrate limitation and product inhibition.
- Dynamic models for gas-liquid mass transfer (kLΓÇïa) and heat removal.
- Techniques for parameter estimation and global sensitivity analysis.
- Case Study: Modeling a high-density perfusion bioreactor, focusing on cell viability, substrate/waste concentrations, and bleed rate optimization.
3. Data-Driven and Hybrid Modeling
- Introduction to data-driven models.
- Integrating Machine Learning (ML) for kinetic parameter estimation.
- Architecture and application of Hybrid Modeling
- Model selection criteria and overfitting prevention.
- Case Study: Building a hybrid model for monoclonal antibody titter prediction, combining a mechanistic growth model with an ML-based correction for nutrient batch variability.
4. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) in Bioreactors
- Fundamentals of fluid flow, mixing, and turbulence models.
- Applying CFD to model shear stress distribution and its impact on cell damage.
- Modeling gas dispersion and its effect on kLΓÇïa and pCO2ΓÇï profiles.
- Meshing strategies and boundary condition setting for complex bioreactor geometries.
- Case Study: Using CFD to evaluate the Scale-Up risk of a novel impeller design based on power input and peak shear stress.
5. Soft Sensors and Real-Time Process Monitoring
- Theory of Soft Sensors and state observers
- Developing multivariate data analysis models for quality prediction.
- Deployment strategies for inferential models in a PAT environment.
- Validation and maintenance of soft sensors.
- Case Study: Designing a soft sensor to estimate the non-measurable CQA of Glycosylation from online process data
6. Modeling of Downstream Processing (DSP) I
- Mechanistic models for adsorption and desorption kinetics.
- Simulation of breakthrough curves and column performance optimization.
- Modeling gradient elution and buffer mixing dynamics.
- Principles of multi-column and Continuous Chromatography.
- Case Study: Simulating a Protein A capture step to optimize load mass and elution buffer concentration for maximum yield and purity.
7. Modeling of Downstream Processing (DSP) II
- Models for dead-end and Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF) processes
- Modeling viral filtration and depth filtration performance.
- Simulation of precipitation, refolding, and crystallization steps.
- Equipment sizing and operational cost estimation for DSP units.
- Case Study: Optimizing the TFF train operation to meet final product concentration and buffer exchange targets.
8. Flowsheet Modeling & Process Integration
- Setting up rigorous mass and energy balances across the entire Flowsheet.
- Using commercial tools for process configuration and flowsheet simulation.
- Convergence techniques for complex recycle loops and integrated processes.
- Defining material specifications, utility requirements, and waste streams.
- Case Study: Integrating USP and DSP models to analyze the impact of upstream harvest titer variability on the entire downstream purification train.
9. Advanced Process Control (APC) and Model Predictive Control (MPC)
- Limitations of PID control in bioprocessing
- Fundamentals of Model Predictive Control.
- Identifying and modeling the process dynamics required for MPC implementation.
- Tuning and deployment of MPC strategies for dual-objective optimization.
- Case Study: Implementing an MPC controller for a fed-batch process to simultaneously regulate glucose concentration and maximize product titer while respecting pH constraints.
10. Scale-Up, Scale-Down, and Technology Transfer
- Theoretical basis for scale-up/scale-down consistency
- Using models to predict performance across different scales
- Model-based approach for defining the Process Operating Range and Design Space.
- Impact of mixing time and transport phenomena on scale-up success.
- Case Study: Predicting the performance of a 2,000L bioreactor based on a 10L pilot-scale model and identifying critical scale-dependent parameters.
11. Techno-Economic Analysis (TEA) & Cost Modeling
- Fundamentals of Capital Expenditure and Operating Expenditure modeling.
- Integrating simulation outputs
- Calculating and comparing Cost of Goods Sold per gram of product.
- Evaluating the financial impact of process intensification and continuous manufacturing.
- Case Study: Performing a side-by-side TEA comparing a traditional batch mAb facility design against a proposed Continuous Bioprocessing design.
12. Model Validation and Regulatory Considerations
- Best practices for Model Verification and Validation
- Statistical methods for assessing model fidelity.
- Documentation and lifecycle management of regulatory models.
- Model's role in supporting ICH Q8-Q12 guidelines and regulatory filings.
- Case Study: Developing a Model Validation report for a QbD model used to set the Control Strategy for a commercial product.
13. Modeling of Continuous Bioprocessing Systems
- Rigorous modeling of continuous processes
- Dynamic simulation of process start-up, steady-state, and shutdown.
- Analyzing the stability and robustness of integrated continuous flowsheets.
- Advanced control loops tailored for continuous operation.
- Case Study: Simulating an integrated continuous mAb process to determine the optimal steady-state operating window.
14. Digital Twin Engineering and Deployment
- Architecture of a Digital Twin for bioprocessing
- Connecting models to real-time data via OPC-UA or other industrial protocols.
- Using the Digital Twin for Virtual Commissioning and What-If scenario testing.
- Leveraging the twin for operator training and decision support.
- Case Study: Designing the structure and implementation plan for a Digital Twin of an existing pilot-scale fermentation facility.
15. Cell & Gene Therapy (CGT) and Novel Modalities
- Modeling challenges unique to CGT
- Process design and simulation for Autologous and Allogeneic cell therapies.
- Application of modeling to Oligonucleotide and mRNA manufacturing processes.
- Risk assessment and scheduling optimization for complex, low-volume/high-value products.
- Case Study: Modeling the upstream process for AAV viral vector production, focusing on the trade-offs between yield and facility utilization.
Training Methodology
The course employs a blended, hands-on methodology to ensure practical skill acquisition and deep conceptual understanding:
- Interactive Lectures
- Software Workshops.
- Case Study-Driven Learning.
- Group Problem Solving.
- Q&A and Expert Discussions.
Register as a group from 3 participants for a Discount
Send us an email: info@datastatresearch.org or call +254724527104
Certification
Upon successful completion of this training, participants will be issued with a globally- recognized certificate.
Tailor-Made Course
We also offer tailor-made courses based on your needs.
Key Notes
a. The participant must be conversant with English.
b. Upon completion of training the participant will be issued with an Authorized Training Certificate
c. Course duration is flexible and the contents can be modified to fit any number of days.
d. The course fee includes facilitation training materials, 2 coffee breaks, buffet lunch and A Certificate upon successful completion of Training.
e. One-year post-training support Consultation and Coaching provided after the course.
f. Payment should be done at least a week before commence of the training, to DATASTAT CONSULTANCY LTD account, as indicated in the invoice so as to enable us prepare better for you.